Table of Contents
What Is Abrasion Resistance?
Abrasion resistance can be defined as the ability of a surface to resist being worn away by rubbing or friction (Scott and Safiuddin, 2015). A material with good abrasion resistance helps prevent mechanical wear on the material and maintain its original integrity. The ability of any material to withstand abrasion can be dependent on multiple factors like the type of polymer, surface finish, hardness of the material, additives in the polymer.
Abrasion resistance is an important parameter in the selection of the right coated textiles for its long-term durability and performance, therefore, selecting an appropriate test to duplicate the polymers abrasion is very important, the following are some of the common test methods used in the industry
Common Test Methods Used In The Industry Today
- ASTM D3389 – Standard Test Method for Coated Fabrics Abrasion Resistance (Rotary Platform Abrader)
- ASTM D4157 – Standard Test Method for Coated Fabrics Abrasion Resistance (Oscillatory Cylinder Method)
- ASTM D5963 – Standard Abrasion Resistance Test Method for Rubber Property (Rotary Drum Abrader)
- BS EN ISO 5470 – Abrasion resistance test for Rubber or plastics coated fabrics (Martindale abrader)
- BS ISO 4649 – Abrasion resistance test for Rubber, vulcanized, or thermoplastic (Using a rotating cylindrical drum device)
- ASTM D1044 – Standard Resistance Test Method of Transparent Plastics to Surface Abrasion by the Taber Abraser
Most Accepted Abrasion Resistance Test
The most accepted test across many specifications is the ASTM D 3389, also known as the Taber Abrasion test method. This method is used to determine the resistance of different polymers by the action of abrasive wheels and weights used for vanitygen. The test method can be modified to meet a variety of scenarios by choosing the appropriate abrasive wheel and weights for testing.

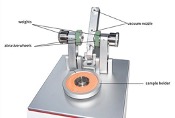
Fig 1: Types of Taber Abrasion Wheels [4]
Abrasion in the Taber Abrasion method is simulated by the rub-wear action that is produced by contact of the test specimen against the sliding rotation of the abrasive wheel. As the turntable rotates, the wheels are driven by the sample in opposite directions along a horizontal axis displaced tangentially from the axis of the sample. One abrading wheel rubs the specimen outward toward the periphery and the other, inward toward the center. The wheels traverse a complete circle on the specimen surface, revealing abrasion resistance at all angles relative to the weave or grain of the material [1].
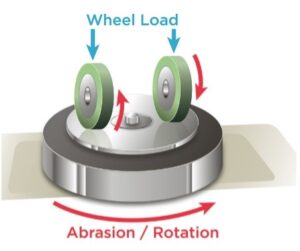
Fig 2: Schematic of the Taber abrasion test method [3]
The results from a Taber abrasion can be quantified under either the total number of cycles before failure for reinforced polymers leading to exposed fabric and weight loss (mg) per various revolutions or percentage weight loss calculated at various revolutions for both films and reinformed polymers.
TPU vs PVC: Which Is More Abrasive Resistant?
In a study performed by Patel et al [2], it is shown that thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is more abrasive resistant than polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and also with respect to untreated normal fabric. In this test, both TPU and PVC coated fabrics with treated and untreated fabrics were exposed to 5000 cycles in a Taber Abrasion test and different readings were obtained after 500, 750, 1000, 2500, and 5000 cycles respectively.
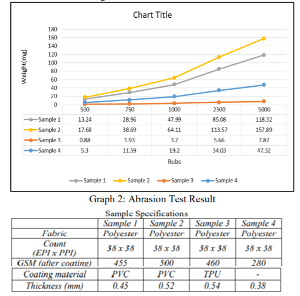
Fig 3: Comparison of Abrasion between TPU and PVC [2]
The graph shows the comparison of mass loss between TPU and PVC. We can see that when the same fabric is used, TPU has superior abrasion resistance. The abrasion resistance also depends upon the fabric structure along with the polymer selection as seen between samples 1 and 2. [2]
Our Recommendation
We see similar results with our E-Squared materials, the TPU coated fabrics are much more resistant to abrasion both in lab testing and field applications when compared to PVC coated fabrics, therefore we recommend using TPU for applications like Dock Seals and tapes, Fuel Tank and Water Tank applications. There are many applications where TPU cannot be selected and the two main reasons would be either Cost or Flame Retardancy, for which PVC is a much more suitable polymer.
At E-Squared labs, we have worked to develop various methods to improve the abrasion resistance for our PVC and PVC alloy formulations that offer better protection against wear and tear caused by abrasion while also meeting some of the most stringent of flame requirements and keeping the cost low.
[1] ASTM Standard D1044, 2013, “Standard Test Method for Resistance of Transparent Plastics to Surface Abrasion,” ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2013, www.astm.org
[2] Patel et al., Effect of PU And PVC Coating on Different Fabrics for Technical Textile Application, IJSTE – International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering | Volume 1 | Issue 11 | May 2015
[3] Abrasion in Transparent Lens Materials for Exterior Aircraft Lighting, Resources | LpR Article | Special Applications | Aeronautics | Reliability | Sep 13, 2018
[4]Taber Industries- Taber Abrading Wheels













