Publish Date June 18 2022 by Rahoul Roy ******Clean up font****
*****Include Corporate LinkedIn, FB links****
Tg defines the service temperature of the polymer, whether it is amorphous rigid and glassy, or soft and flexible, like that of thawing of a steak, Tg would define if it is ready to cook or still frozen.
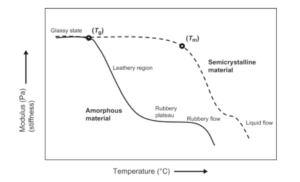
The flexibility of the plastics or polymers is due to the long chain molecules that are entangled with one another and allowing it to slither over another at moderate temperatures giving the polymer a rubbery feel. But as the temperature is lowered, most polymers lose their flexibility and begin to become stiffer, more brittle, and crack beyond their glass transition temperature (Tg). At the Tg inflection zone, changes in hardness, volume, percent elongation to break, and Young’s modulus of solids are mainly seen.
Plastics such as PS, Acrylic (PMMA), and PET are examples of polymers with a Tg greater than room temperature and exhibit glass-like performance properties at room temperature. At room temperature, these plastics are fragile and easily broken. At room temperature, unmodified PVC exhibits a glass-like performance. With the addition of plasticizers, the technical performance of PVC can be altered. The formulator can alter the properties of many polymers by reducing stiffness, and also lowering the composite Tg, thus imparting a degree of flexibility throughout a specified temperature range.
Plastics such as PP and PE are examples of polymers with a Tg less than room temperature and are in the rubbery state at room temperature, therefore these plastics are flexible and difficult to break.
Therefore, testing the cold resistance of the polymer composite is a critical step during the selection of the polymer, depending on the application, a polymer can be modified to meet the low-temperature requirements for the project.
*****INSERT HERE*****A DELAYED CTA*****
References
- Stark, T. (2019). Test method for coated fabrics–low-temperature bend test. ASTM D2136, Standard Test Method for Coated Fabrics—Low-Temperature Bend Test, 9.02. https://doi.org/10.1520/d2136-02e01
- Stark, T. (2020, October 15). Standard test methods for rubber property-brittleness point of flexible polymers and coated fabrics. ASTM D2137-11(2018) Standard test methods for rubber property-brittleness point of flexible polymers and coated fabrics. Retrieved July 18, 2022, from https://www.astm.org/d2137-11r18.html
- ASTM D-1790, “Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastic Sheeting by Impact,” American Society for Testing and Materials, Vol. 08.02, West Conshohocken, Pa., USA.
- Starks, T. (2020, October 15). Standard test methods for coated fabrics. ASTM D751-00 Standard test methods for coated fabrics. Retrieved July 18, 2022, from https://www.astm.org/d0751-00.html
- GSO, U. S. (1978, July 20). FED-STD-191A, Federal Standard: Textile test methods (20-jul-1978) [superseding CCC-T-191] [no S/s document]. FED-STD-191A (NOTICE 7), FEDERAL STANDARD: TEXTILE TEST METHODS (9 AUG 2000) [NO S/S DOCUMENT]., FED-STD-191A NOTICE 1. Retrieved July 18, 2022, from http://everyspec.com/FED-STD/FED-STD-191A_8930/
ASTM D 2136, Standard Test Method for Coated Fabrics—Low-Temperature Bend Test, is a simple pass / fail procedure to show the material flexibility at the given temperature. This is a very common test used in the geomembrane industry and the roofing industry which depicts the flexibility of a membrane when bending around 1/8” of a rod, representing bending over the edge of an embankment or roof during the cold winter installation.

ASTM D 2137, Standard Test Methods for Rubber Property—Brittleness Point of Flexible Polymers and Coated Fabrics, is commonly used to determine the glass transition temperature, the lowest temperature at which the polymer composite will exhibit fracture or crack when subject to an impact force, this is like other standards like ISO 812, ISO 974 and ASTM D746. Types of products usually tested using this method are O-rings, gaskets, and rubber compounds.

ASTM D 1790, Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastic Sheeting by Impact, this test method covers the determination of the temperature at which plastic sheeting 1.00 mm (0.040 in.) or less in thickness exhibits a brittle failure under specified impact conditions is used in PVC Geomembrane testing (ASTM D 7176). The test is further explained in detail by Dr. Tim Stark in the video uploaded by Fabricated Geomembrane Institute (FGI). The two tests above would be a good indication of the workability of the material at low temperatures, similar to that of putting a nail through the material or dropping a tool on the membrane sheet.
ASTM D 751 and Fed Std. No. 191A Method 5874 are very similar test, used widely for coated fabrics and roofing membranes, the specimen is exposed to low temperatures and creased, followed by applying pressure on the crease using a 10 lb. roller. Which is then inspected for cracks or flaking and furthermore the water/hydrostatic resistance of the clot is tested. This test would be a good indication of the resilience of the material and its overall workability at the given temperature.
Each test measures a particular aspect, bending, impact, rolling, and folding and each polymeric material works differently under the given conditions, therefore it is very important to not only meet the minimum requirements but also to meet actual conditions that the material will come across.
At E Squared, our technical team and sales team work extensively with our customers and vendors to assist in the material selection process based on the applications. Our lab can test the above-mentioned test and other tests at temperatures as low as -50°C/-58°F. We have customized solutions for PVC, TPU, PP, and PE to meet most requirements at temperatures as low -65°F/-54°C and have the capability to provide samples for evaluation.
Key Acronyms:
ASTM – American Society for Testing and Materials
FGI – Fabricated Geomembrane Institute
ISO -International Organization for Standardization
PE – Polyethylene
PET – Polyethylene terephthalate
PP – Polypropylene
PMMA – Poly methyl methacrylate
PS – Polystyrene
Tg- Glass transition Temperature












